The disease occurs year-round on species such as black tiger prawn, whiteleg shrimp, giant river prawn, etc. The disease can occur in all stages of growing, from egg to adult shrimp.
Luminous Bacteria Disease thrives in nutrient-rich water with organic substances, high salinity, low dissolved oxygen, and spreads quickly in hot weather.
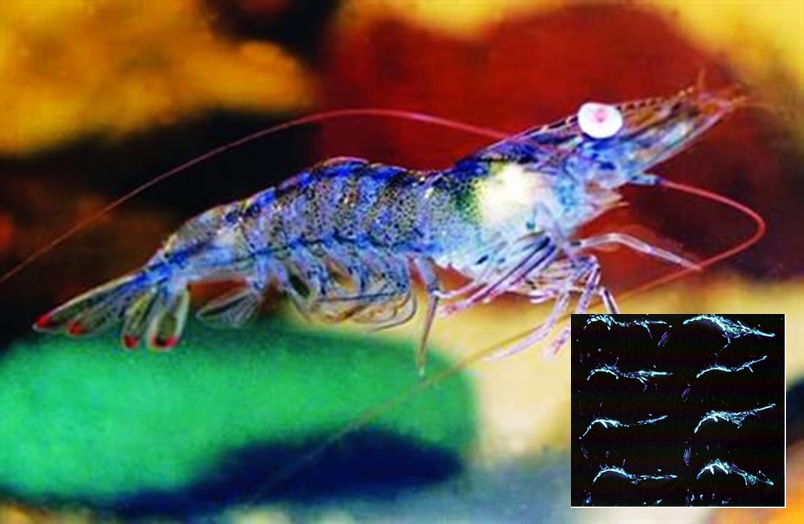
Cause
– The bacteria are in the group of Luminescencet Vibrio; the main and most dangerous is Vibrio harveyi. These bacteria have the enzyme Luciferase that causes light emission.
– In the group of Gram-negative bacteria, they grow in the salinity of 10-40ppt (strongest in the salinity of 20-30 ppt).
– These bacteria are resistant to many antibiotics.
– Disease can be infected from hatcheries, nurseries into farming pond. In hatchery, pathogen is spread mainly through mothers-to-larvae intestine in the reproductive phase
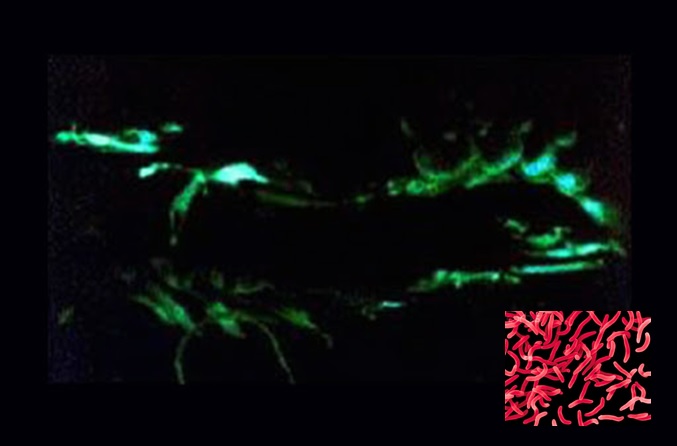
Symptoms
– Shrimp is weak, swims in a non-directional path, appears along edges, pond corners, and responds slowly.
– Shrimp body and gill have dark, dirty and muddy color. Liver is inflamed, shrink, and loses its digestive function for shrimp.
– Shrimp reduces eating. There are no feed and feces in shrimp intestine. Shrimp feces in the feeding tray are not much.
– Shrimp head and body glow in white-green colors in the dark.
– Observe under the microscope, glowing bacteria are seen to be moving in shrimp muscle and blood.
– There are little luminous points on shrimp meat
– Shrimp grows slowly. Surface fouling may occur in shrimp gills and shells.
– Shrimps die dispersedly depending on the severity of the disease. If the disease infects 100% shrimps during the beginning 45 days of culture, shrimps may die in series.
– Infected shrimp larvae have milky color. If they are seriously infected, larvae will submerse under the nursery tanks and die in a massive amount.
Diagnostic methods:
– Recognize the symptoms.
– Tested by TCBS Agar test kit (use thiosulfate citrate bile sucrose agar environment) to detect the bacteria
PREVENTION AND TREATMENT
- Hatchery:
– Thoroughly clean the incubator and hatching tank.
– Regularly disinfect tools.
– Treatment of water by UV, chlorine, ozone
– Treatment of artemia eggs with chlorine
- Shrimp seed:
– Choose healthy, disease-free broodstock.
– Check by PCR
– Check the stress and health of the breed, weak shrimp with formol,
– Stocking with suitable stocking density
- Rearing Pond / Farming Pond
– Before the farming season, the pond must be renovated: dredge the bottom mud, apply lime, and dry the pond
– Disinfection in ponds and water with Chlorine 30ppm or B.K.C 1-2ppm or potassium permanganate KMnO4
– Kill intermediate hosts, limit crabs, crabs, and snails in ponds. Remove all dead shrimp from the pond.
– Use probiotics to improve pond bottom and treat water daily 7 days before stocking shrimp.
- Prevention:
– Salinity:
Do not raise shrimp at too high salinity. Lower the salinity to inhibit luminous bacteria.
– Water temperature:
In the summer, maintain the water level in the pond from 1.2 – 1.5m and the clarity of the water from 30-40cm to limit the possibility of heat rise.
– Keep the environment stable:
Check water quality (pH, kH, turbidity, color, algae) and pond bottom regularly for timely treatment.
- Increase aeration run.
- Use probiotics, granulated sugar, periodically.It is necessary to keep the environment stable so that the algae do not simultaneously discolor the water and the bottom mud. Development of a group of green algae (chlorella) to control the growth of Vibrio harveyi .
– Reduce organic matter in water:
Check the feeder every day, adjust the feed appropriately, do not leave excess food to contaminate the water and pond bottom.
Periodically change water, siphon bottom, suck mud, to reduce organic matter in the pond.
– Health care and disease prevention for shrimp:
Adding vitamin C, multivitamins, digestive enzymes and trace minerals to the feed to create antibodies, help shrimp have resistance, reduce stress for shrimp, especially when there is a change in water environment or weather fluctuations.
Since shrimp is 21 days old, periodically check vibrio in water and shrimp every 7 days. Vibrio in water must be less than 102 cells/cc and no bacteria in shrimp liver
- Handling when shrimp is infected:
– Use antibiotics: use the right medicine, the right dose, the right time. The use of antibiotics is only effective when the disease is detected early.
– Add multivitamins and digestive enzymes to food.
– Disinfect water in the pond and disinfect tools and equipment.
 Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt Indonesia
Indonesia